This article is part of a series.
View all 17 parts
- Part 1 – The Hunter S. Thompson Board -- Arduino Mega Mini
- Part 2 – Make an ADXL345 Breakout Board
- Part 3 – Mega Mini Motor Shield (M^3)
- Part 4 – My Eagle PCB Walkthrough
- Part 5 – Populating and Programming and APM
- Part 6 – Incomplete Works
- Part 7 – HM-10
- Part 8 – Jot
- Part 9 – Homemade Pulse Sensor
- Part 10 – ATtiny Adventure -- I2C on ATtiny 84/85
- Part 11 – ATtiny Bitsy Spider
- Part 12 – This Article
- Part 13 – Scarab
- Part 14 – The Valdez Mutant -- LPC1114 QFN
- Part 15 – Lab Controller PCB
- Part 16 – Lab Controller v05-09
- Part 17 – Robber Board
Originally posted on www.letsmakerobots.com
Awhile back Sparkfun posted a new product, their MiniMoto breakout board. It breaks out the DRV8830 IC, which is a serially controlled (I2C) H-Bridge. I thought the chip was nifty. A few problems though,
- Sparkfun's breakout was 25x25mm for one bridge. If I added another and then an Arduino Pro Mini it'd lose smallness.
- It's $9.95
- It's not on a purple board :)
So, I set out to make a robot controller with it that was smaller than a Sparkfun breakout. What I ended up with is a little bitch I refer to a Kobold.

The board is pretty straightforward. It has an ATtiny 85 that acts as an I2C Master using the SoftI2CMaster library. This allows the Tiny 85 to control two motors using only two pins, leaving three for your pleasure.
My end goal will be to build a shield for it and hook up a HM-10 to make it a little wireless tethered bot. This would bring me down to one pin, which I'm sure will be some sort of range finder or feeling sensor.
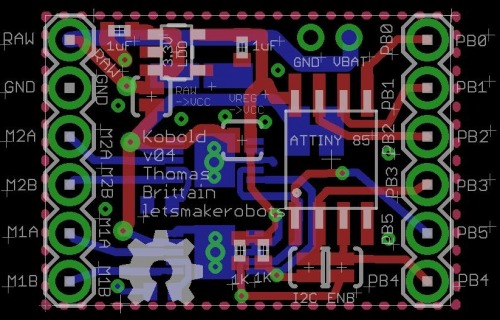
The BOM:
- 1 x ATtiny 85 SOIC $1.21
- 2 x DRV8830 MSOP-10 $5.10
- 2 x .33 Ohm 0402 $.86
- 1 x 1uF 0402
- 2 x 4.7k Res. 0402
- 1 x Kobold PCB $2.50 (for three)
Total: $9.76
The board can be programmed with an Arduino ISP:

Now, I just need to make a robot with it :)
I'm currently working on a second iteration to correct some problems. I'll also add a few features, like my pogo-pin programming interface. The shield I have designed for it will also include a charging circuit and probably a SMD step-up circuit that should convert a LiPo to a nice 5v.
Anyway, work in progress...just thought I'd share.
If anyone is interested in this board, please wait a few iterations. I get worried I'm making blue-smoke with someone else's money. :)
Here is the code running in the video:
//Sample Code for the Kobold Board.
#define NO_INTERRUPT 1
#define I2C_TIMEOUT 100
#define SDA_PORT PORTB
#define SDA_PIN 4
#define SCL_PORT PORTB
#define SCL_PIN 3
#include <SoftI2CMaster.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
void CPUSlowDown(int fac) {
// slow down processor by a fac
CLKPR = _BV(CLKPCE);
CLKPR = _BV(CLKPS1) | _BV(CLKPS0);
}
boolean writeSpeed(byte addr, int speedx)
{
//This should clear the fault register.
byte regValue = 0x08;
//Clear the fault status, in case there is one.
if (!i2c_start(addr | I2C_WRITE)) {
return false;
}
if (!i2c_write(0x01)) { //0x01 = We want to write.
return false;
}
if (!i2c_write(regValue)) { //Write the clear bye for fault register.
return false;
}
i2c_stop(); //Stop transmission.
//Let's convert the integer given us into a byte.
regValue = (byte)abs(speedx); //Convert 0-63 to byte value to set speed.
if (regValue > 63) regValue = 63; // Cap the value at 63.
regValue = regValue<<2; // Left shift to make room for bits 1:0
if (speedx < 0) regValue |= 0x01; // Set bits 1:0 based on sign of input.
else regValue |= 0x02; //A negative number for reverse and positive for forward.
//Now, let's move this sucker.
//Sets the i2c slave address
if (!i2c_start(addr | I2C_WRITE)) {
return false;
}
//0x00 = We want to write something.
if (!i2c_write(0x00)) {
return false;
}
//Writes the byte which had been converted from an integer that was passed this function. Annnnd! The motor moves!
if (!i2c_write(regValue)) {
return false;
}
i2c_stop();
return true;
}
boolean writeStop(byte addr)
{
if (!i2c_start(addr | I2C_WRITE)) {
return false;
}
if (!i2c_write(0x00)) {
return false;
}
if (!i2c_write(0x00)) {
return false;
}
i2c_stop();
return true;
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup(void) {
#if I2C_CPUFREQ == (F_CPU/8)
CPUSlowDown();
#endif
}
void loop(void){
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++){
delay(100);
if (!writeSpeed(0xC0, 10));
if (!writeSpeed(0xCE, 10));
delay(1000);
if (!writeStop(0xC0) );
if (!writeStop(0xCE) );
delay(1000);
if (!writeSpeed(0xC0, -10));
if (!writeSpeed(0xCE, -10));
delay(1000);
if (!writeStop(0xC0) );
if (!writeStop(0xCE) );
delay(100);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++){
delay(100);
if (!writeSpeed(0xC0, 14));
if (!writeSpeed(0xCE, 34));
delay(1000);
if (!writeStop(0xC0) );
if (!writeStop(0xCE) );
delay(1000);
if (!writeSpeed(0xC0, -14));
if (!writeSpeed(0xCE, -34));
delay(1000);
if (!writeStop(0xC0) );
if (!writeStop(0xCE) );
delay(100);
}
}